16
16
0
Posted >1 y ago
Responses: 6
The basic background information for this video's story is the sniper battle between the legendary American sniper Carlos Hathcock (AKA "White Feather") and ...
Thanks CW5 Jack Cardwell for reminding us about legendary USMC sniper Gunnery Sergeant Carlos Norman Hathcock II
Images: GySgt Carlos Hathcock II; GySgt Carlos Norman Hathcock II; GYSGT Carlos Hathcock Vietnam Hunt Club-5501
Background from militaryhallofhonor.com/honoree-record.php?id=2614
"Carlos Norman Hathcock II
Gunnery Sergeant, U.S. Marine Corps
Carlos Norman Hathcock II was born on 20 May 1942 in Little Rock, AR. He grew up in rural Arkansas, living with his grandmother after his parents separated. He took to shooting and hunting at an early age, partly out of necessity to help feed his poor family. He would go into the woods with his dog and pretend to be a soldier and hunt imaginary Nazis in his "own little Germany." He would hunt at that early age with a rifle that his father had brought back from Europe during World War II. Hathcock dreamed of being a Marine throughout his childhood, and so on 20 May 1959, at the age of 17, he enlisted in the U.S. Marine Corps.
Before deploying to Vietnam, Hathcock had won shooting championships, including matches at Camp Perry and the Wimbledon Cup. In 1966 Hathcock started his deployment in Vietnam as an MP and later became a sniper after Captain Edward James Land pushed the Marines into raising snipers in every platoon. Land later recruited Marines who had set their own records in sharpshooting; he quickly found Hathcock, who had won the Wimbledon Cup, the most prestigious prize for long-range shooting, at Camp Perry in 1965.
During the Vietnam War Hathcock had 93 confirmed kills of North Vietnamese Army and Viet Cong personnel. (During the Vietnam War, kills had to be confirmed by an acting third party, who had to be an officer, besides the sniper's spotter. Snipers often did not have an acting third party present, making confirmation difficult, especially if the target was behind enemy lines, as was usually the case.) He is ranked fifth, behind U.S. Marine Corps snipers Eric R. England and Chuck Mawhinney and U.S. Army snipers Christopher S. Kyle and Adelbert Waldron, on the list of most confirmed kills for an American sniper.
Confrontations with NVA Snipers
The North Vietnamese Army (NVA) put a bounty of $30,000 on Hathcock's life for killing so many of their men. Rewards put on U.S. snipers by the NVA typically ranged from $8 to $2,000. Hathcock held the record for highest bounty and killed every Vietnamese marksman who sought it. The Viet Cong and NVA called Hathcock Lông Trắng, translated as "White Feather," because of the white feather he kept in a band on his bush hat. After a platoon of trained Vietnamese snipers was sent to hunt down "White Feather," many Marines in the same area donned white feathers to deceive the enemy. These Marines were aware of the impact Hathcock's death would have and took it upon themselves to make themselves targets in order to confuse the counter-snipers.
One of Hathcock's most famous accomplishments was shooting an enemy sniper through the enemy's own scope, hitting him in the eye and killing him. Hathcock and John Roland Burke, his spotter, were stalking the enemy sniper in the jungle near Hill 55, the firebase from which Hathcock was operating. The sniper had already killed several Marines and was believed to have been sent specifically to kill Hathcock. When Hathcock saw a flash of light (light reflecting off the enemy sniper's scope) in the bushes, he fired at it, shooting through the scope and killing the sniper. Surveying the situation, Hathcock concluded that the only feasible way he could have put the bullet straight down the enemy's scope and through his eye would have been if both snipers were zeroing in on each other at the same time and Hathcock fired first, which gave him only a few seconds to act. Given the flight time of rounds at long ranges, both snipers could have simultaneously killed one another. Hathcock took possession of the dead sniper's rifle, hoping to bring it home as a "trophy," but after tagging the rifle it was stolen from the armory.
"It was a one in a million shot. I could probably shoot a whole box of ammunition and never hit him again." Carlos Hathcock.
A female Viet Cong sniper, platoon commander, and interrogator known as "Apache" because of her methods of torturing U.S. Marines and ARVN troops and letting them bleed to death, was killed by Hathcock. This was a major morale victory as "Apache" was terrorizing the troops around Hill 55.
Assassination of a NVA Commanding General
Hathcock only once removed the white feather from his bush hat while deployed in Vietnam. During a volunteer mission days before the end of his first deployment, he crawled over 1,500 yards of field to shoot an NVA commanding general. He was not informed of the details of the mission until he accepted it. This effort took four days and three nights, without sleep, of constant inch-by-inch crawling. Hathcock said he was almost stepped on as he lay camouflaged with grass and vegetation in a meadow shortly after sunset. At one point he was nearly bitten by a Bamboo Viper, but had the presence of mind to avoid moving and giving up his position. As the general exited his tent, Hathcock fired a single shot that struck the general in the chest, killing him. He had to crawl back instead of run when soldiers started searching, and later regretted taking the mission, for in the aftermath of the assassination the NVA doubled their attacks in the area, apparently in retaliation for their general being killed and leading to an increase in American casualties.
After the arduous mission of killing the general, Hathcock returned to the U.S. in 1967. However, he missed the Marine Corps and returned to Vietnam in 1969, where he took command of a platoon of snipers.
Medical Evacuation
Hathcock's career as a sniper came to a sudden end along Route 1, north of LZ Baldy in September 1969, when the Amtrack he was riding on, an LVT-5, struck an anti-tank mine. Hathcock pulled seven Marines off the flame-engulfed vehicle and was severely burned before jumping to safety. Nearly 30 years later, he would receive the Silver Star for this action. All eight injured marines were medevaced to the USS Repose (AH-16), then to a Naval Hospital in Tokyo, and ultimately to the burn center at Brooke Army Medical Center in San Antonio, TX.
Post-Vietnam
After returning to active duty, Hathcock helped establish the school for training Marine snipers, the Marine Corps Scout Sniper School, at the Marine base in Quantico, VA. Due to his extreme injuries suffered in Vietnam, he was in nearly constant pain, but he continued to dedicate himself to teaching snipers. In 1975, Hathcock's health began to deteriorate and he was diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis. He stayed in the Corps but his health continued to decline and was forced to retire just 55 days short of the 20 years that would have made him eligible for full retirement pay. Being medically retired, he received 100% disability. He would have received only 50% of his final pay grade had he retired after 20 years. He fell into a state of depression when he was forced out of the Marines because he felt as if the service kicked him out. During this depression, his wife Jo nearly left him, but decided to stay. Hathcock eventually picked up the hobby of shark fishing with the locals, which helped him overcome his depression. Hathcock often paid visits to the sniper training facility at Quantico, where he was welcomed by students and instructors alike as being "bigger than life" due to his status in shooting circles.
Weaponry
Hathcock generally used the standard sniper rifle: the Winchester Model 70 .30-06 caliber rifle with the standard 8-power Unertl scope. On some occasions, however, he used a different weapon: the Browning M2 machine gun, on which he mounted a 10X Unertl scope, using a bracket of his own design. Hathcock made a number of kills with this weapon in excess of 1,000 yards, including his record for the longest confirmed kill at 2,286 yards. Hathcock carried a Colt M1911A1 pistol as a sidearm.
Medals and Awards
Silver Star Medal
Purple Heart
Navy and Marine Corps Commendation Medal
Navy and Marine Corps Achievement Medal
Combat Action Ribbon
Marine Good Conduct Medal with Silver Star
National Defense Service Medal
Vietnam Service Medal
Vietnam Cross of Gallantry
Vietnam Campaign Medal
Honors
Hathcock remains a legend in the U.S. Marine Corps. The Gunnery Sergeant Carlos Hathcock Award is presented annually to the Marine who does the most to promote marksmanship training. A sniper range is named for Hathcock at Camp Lejeune, NC.
In 1967, Hathcock set the record for the longest combat kill. He used a Browning M2 machine gun mounting a telescopic sight at a range of 2,500 yards, taking down a single Vietcong guerilla. This was not exceeded until Canadian snipers from the 3rd Bn. PPCLI during the War in Afghanistan in 2002. Hathcock was one of several individuals to utilize the Browning M2 machine gun in the sniping role. This success led to the adoption of the .50 BMG cartridge as a viable sniper round. Sniper rifles have since been designed around and chambered in this caliber since the 1970s. The Canadian Army snipers from the PPCLI also used the .50 BMG round in their record breaking shots.
Springfield Armory designed a highly accurized version of their M1A Supermatch rifle with a McMillan Stock and match grade barrel and dubbed it the "M-25 White Feather." The rifle had a likeness of Hathcock's signature and his "White Feather Logo" marked on the receiver.
Turner Saddlery similarly honored Hathcock by producing a line of leather rifle slings based on his design. The slings are embossed with Hathcock's signature.
On 9 March 2007, the rifle and pistol complex at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar was officially renamed the Carlos Hathcock Range Complex.
Books (Non-Fiction)
Hathcock was the subject of a number of books including:
Chandler, Roy F. (1997). White feather: Carlos Hathcock USMC scout sniper : an authorized biographical memoir (1997 ed.). Iron Brigade Armory Publishing. Total pages: 277
Henderson, Charles (2001). Marine Sniper: 93 Confirmed Kills (2001 ed.). Berkley Books. Total pages: 315
Henderson, Charles W. (2003). Silent Warrior (2003 ed.). Berkley Books. Total pages: 336
Sasser, Charles; Roberts, Craig (1990). One Shot, One Kill (1990 ed.). Pocket Books. Total pages: 288
Fictional Works
Hathcock's career as a sniper has been used as a basis for a variety of fictional snipers from the "shooting through the scope incident" to the number of kills he made. There is a reference to Hathcock in the television show NCIS during the episode "One Shot One Kill," when a small white feather is found at the crime scenes of a sniper's victims. Gibbs, a former Marine, credits Hathcock with "39 confirmed kills," apparently having transposed the digits of Hathcock's actual 93 confirmed kills.
The protagonist of Stephen Hunter's Bob Lee Swagger Series consisting of the novels Point of Impact, Black Light, Time to Hunt and I, Sniper is loosely based on Carlos Hathcock (Hathcock is alluded to in the book as "Gunny Sgt Carl Hitchcock".)
The 1993 movie Sniper, featuring actor Tom Berenger, is based on Hathcock's exploits in Vietnam.
In JAG, Season 1, Episode 16 ("High Ground"), Gunnery Sergeant Ray Crockett (portrayed by Stephen McHattie) is based on Hathcock. The Gunny is a sniper instructor at Quantico Virginia who believes that he is being "forced out of the service" short of his retirement. He makes the statement that he "wrote most of the book" on sniper operations. The character, Rabb, refers to an incident where the Gunny pins down an NVA unit by killing their officer with the first shot. Lastly, Gunny Crockett is a winner of The Wimbledon Cup.
In the fourth episode of the first season of the CBS show Criminal Minds: Suspect Behavior, the criminal being chased by the Behavioral Analysis Unit's red cell team is a long-distance sniper killer, (played by Noel Fisher). Fisher sends Mick Rawson (played by Matt Ryan) of the BAU team a package containing a pager which he uses to notify Rawson of his next kills; he signs the package "Carlos Hathcock," which Rawson explains by sharing the tale of Hathcock's 93 kills and an incident during the Vietnam War in which he was put up against the best sniper of the NVA known only as 'Cobra'. (thus mimicking the incident since Rawson is also a skilled sniper shooter).
Civilian Life
Hathcock once said that he survived in his work because of an ability to "get in the bubble," to put himself into a state of "utter, complete, absolute concentration," first with his equipment, then his environment, in which every breeze and every leaf meant something, and finally on his quarry. After the war, a friend showed Hathcock a passage written by Ernest Hemingway: "Certainly there is no hunting like the hunting of man, and those who have hunted armed men long enough and like it, never really care for anything else thereafter." He copied Hemingway's words on a piece of paper. "He got that right," Hathcock said. "It was the hunt, not the killing." Hathcock said in a book written about his career as a sniper: "I like shooting, and I love hunting. But I never did enjoy killing anybody. It's my job. If I don't get those bastards, then they're gonna kill a lot of these kids dressed up like Marines. That's the way I look at it."
Hathcock's son, Carlos Hathcock III, would later enlist in the Marine Corps; he retired from the Marine Corps as a Gunnery Sergeant after following in his father's footsteps as a shooter, and became a member of the Board of Governors of the Marine Corps Distinguished Shooters Association.
Personal
Hathcock married Jo Winstead on 20 November 1962. Jo gave birth to a son, whom they named Carlos Norman Hathcock III.
Death and Burial
Gunnery Sergeant Carlos Norman Hathcock II died on 23 February 1999, in Virginia Beach, VA, after a long struggle with multiple sclerosis. He is buried at Woodlawn Memorial Gardens in Norfolk, VA."
he basic background information for this video's story is the sniper battle between the legendary American sniper Carlos Hathcock (AKA "White Feather") and the infamous NVA (North Vietnamese Army) sniper called "Cobra". White Feather and his spotter, John Burke, trail the deadly sniper through the jungle near the military base of Hill 55 in Da Nang, Vietnam, and they eventually manage to defeat the lone sniper by shooting through the scope of the NVA sniper.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S-prw33dyt0
FYI COL Mikel J. Burroughs LTC Stephen C. LTC Ivan Raiklin, Esq. Capt Seid Waddell Capt Tom Brown CW5 (Join to see) SGM David W. Carr LOM, DMSM MP SGT MSG Andrew White SFC William Farrell SSgt Robert Marx SSgt (Join to see) TSgt Joe C. SGT John " Mac " McConnell SP5 Mark Kuzinski SPC (Join to see) SrA Christopher Wright Cpl Joshua Caldwell SFC Joe S. Davis Jr., MSM, DSL
Images: GySgt Carlos Hathcock II; GySgt Carlos Norman Hathcock II; GYSGT Carlos Hathcock Vietnam Hunt Club-5501
Background from militaryhallofhonor.com/honoree-record.php?id=2614
"Carlos Norman Hathcock II
Gunnery Sergeant, U.S. Marine Corps
Carlos Norman Hathcock II was born on 20 May 1942 in Little Rock, AR. He grew up in rural Arkansas, living with his grandmother after his parents separated. He took to shooting and hunting at an early age, partly out of necessity to help feed his poor family. He would go into the woods with his dog and pretend to be a soldier and hunt imaginary Nazis in his "own little Germany." He would hunt at that early age with a rifle that his father had brought back from Europe during World War II. Hathcock dreamed of being a Marine throughout his childhood, and so on 20 May 1959, at the age of 17, he enlisted in the U.S. Marine Corps.
Before deploying to Vietnam, Hathcock had won shooting championships, including matches at Camp Perry and the Wimbledon Cup. In 1966 Hathcock started his deployment in Vietnam as an MP and later became a sniper after Captain Edward James Land pushed the Marines into raising snipers in every platoon. Land later recruited Marines who had set their own records in sharpshooting; he quickly found Hathcock, who had won the Wimbledon Cup, the most prestigious prize for long-range shooting, at Camp Perry in 1965.
During the Vietnam War Hathcock had 93 confirmed kills of North Vietnamese Army and Viet Cong personnel. (During the Vietnam War, kills had to be confirmed by an acting third party, who had to be an officer, besides the sniper's spotter. Snipers often did not have an acting third party present, making confirmation difficult, especially if the target was behind enemy lines, as was usually the case.) He is ranked fifth, behind U.S. Marine Corps snipers Eric R. England and Chuck Mawhinney and U.S. Army snipers Christopher S. Kyle and Adelbert Waldron, on the list of most confirmed kills for an American sniper.
Confrontations with NVA Snipers
The North Vietnamese Army (NVA) put a bounty of $30,000 on Hathcock's life for killing so many of their men. Rewards put on U.S. snipers by the NVA typically ranged from $8 to $2,000. Hathcock held the record for highest bounty and killed every Vietnamese marksman who sought it. The Viet Cong and NVA called Hathcock Lông Trắng, translated as "White Feather," because of the white feather he kept in a band on his bush hat. After a platoon of trained Vietnamese snipers was sent to hunt down "White Feather," many Marines in the same area donned white feathers to deceive the enemy. These Marines were aware of the impact Hathcock's death would have and took it upon themselves to make themselves targets in order to confuse the counter-snipers.
One of Hathcock's most famous accomplishments was shooting an enemy sniper through the enemy's own scope, hitting him in the eye and killing him. Hathcock and John Roland Burke, his spotter, were stalking the enemy sniper in the jungle near Hill 55, the firebase from which Hathcock was operating. The sniper had already killed several Marines and was believed to have been sent specifically to kill Hathcock. When Hathcock saw a flash of light (light reflecting off the enemy sniper's scope) in the bushes, he fired at it, shooting through the scope and killing the sniper. Surveying the situation, Hathcock concluded that the only feasible way he could have put the bullet straight down the enemy's scope and through his eye would have been if both snipers were zeroing in on each other at the same time and Hathcock fired first, which gave him only a few seconds to act. Given the flight time of rounds at long ranges, both snipers could have simultaneously killed one another. Hathcock took possession of the dead sniper's rifle, hoping to bring it home as a "trophy," but after tagging the rifle it was stolen from the armory.
"It was a one in a million shot. I could probably shoot a whole box of ammunition and never hit him again." Carlos Hathcock.
A female Viet Cong sniper, platoon commander, and interrogator known as "Apache" because of her methods of torturing U.S. Marines and ARVN troops and letting them bleed to death, was killed by Hathcock. This was a major morale victory as "Apache" was terrorizing the troops around Hill 55.
Assassination of a NVA Commanding General
Hathcock only once removed the white feather from his bush hat while deployed in Vietnam. During a volunteer mission days before the end of his first deployment, he crawled over 1,500 yards of field to shoot an NVA commanding general. He was not informed of the details of the mission until he accepted it. This effort took four days and three nights, without sleep, of constant inch-by-inch crawling. Hathcock said he was almost stepped on as he lay camouflaged with grass and vegetation in a meadow shortly after sunset. At one point he was nearly bitten by a Bamboo Viper, but had the presence of mind to avoid moving and giving up his position. As the general exited his tent, Hathcock fired a single shot that struck the general in the chest, killing him. He had to crawl back instead of run when soldiers started searching, and later regretted taking the mission, for in the aftermath of the assassination the NVA doubled their attacks in the area, apparently in retaliation for their general being killed and leading to an increase in American casualties.
After the arduous mission of killing the general, Hathcock returned to the U.S. in 1967. However, he missed the Marine Corps and returned to Vietnam in 1969, where he took command of a platoon of snipers.
Medical Evacuation
Hathcock's career as a sniper came to a sudden end along Route 1, north of LZ Baldy in September 1969, when the Amtrack he was riding on, an LVT-5, struck an anti-tank mine. Hathcock pulled seven Marines off the flame-engulfed vehicle and was severely burned before jumping to safety. Nearly 30 years later, he would receive the Silver Star for this action. All eight injured marines were medevaced to the USS Repose (AH-16), then to a Naval Hospital in Tokyo, and ultimately to the burn center at Brooke Army Medical Center in San Antonio, TX.
Post-Vietnam
After returning to active duty, Hathcock helped establish the school for training Marine snipers, the Marine Corps Scout Sniper School, at the Marine base in Quantico, VA. Due to his extreme injuries suffered in Vietnam, he was in nearly constant pain, but he continued to dedicate himself to teaching snipers. In 1975, Hathcock's health began to deteriorate and he was diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis. He stayed in the Corps but his health continued to decline and was forced to retire just 55 days short of the 20 years that would have made him eligible for full retirement pay. Being medically retired, he received 100% disability. He would have received only 50% of his final pay grade had he retired after 20 years. He fell into a state of depression when he was forced out of the Marines because he felt as if the service kicked him out. During this depression, his wife Jo nearly left him, but decided to stay. Hathcock eventually picked up the hobby of shark fishing with the locals, which helped him overcome his depression. Hathcock often paid visits to the sniper training facility at Quantico, where he was welcomed by students and instructors alike as being "bigger than life" due to his status in shooting circles.
Weaponry
Hathcock generally used the standard sniper rifle: the Winchester Model 70 .30-06 caliber rifle with the standard 8-power Unertl scope. On some occasions, however, he used a different weapon: the Browning M2 machine gun, on which he mounted a 10X Unertl scope, using a bracket of his own design. Hathcock made a number of kills with this weapon in excess of 1,000 yards, including his record for the longest confirmed kill at 2,286 yards. Hathcock carried a Colt M1911A1 pistol as a sidearm.
Medals and Awards
Silver Star Medal
Purple Heart
Navy and Marine Corps Commendation Medal
Navy and Marine Corps Achievement Medal
Combat Action Ribbon
Marine Good Conduct Medal with Silver Star
National Defense Service Medal
Vietnam Service Medal
Vietnam Cross of Gallantry
Vietnam Campaign Medal
Honors
Hathcock remains a legend in the U.S. Marine Corps. The Gunnery Sergeant Carlos Hathcock Award is presented annually to the Marine who does the most to promote marksmanship training. A sniper range is named for Hathcock at Camp Lejeune, NC.
In 1967, Hathcock set the record for the longest combat kill. He used a Browning M2 machine gun mounting a telescopic sight at a range of 2,500 yards, taking down a single Vietcong guerilla. This was not exceeded until Canadian snipers from the 3rd Bn. PPCLI during the War in Afghanistan in 2002. Hathcock was one of several individuals to utilize the Browning M2 machine gun in the sniping role. This success led to the adoption of the .50 BMG cartridge as a viable sniper round. Sniper rifles have since been designed around and chambered in this caliber since the 1970s. The Canadian Army snipers from the PPCLI also used the .50 BMG round in their record breaking shots.
Springfield Armory designed a highly accurized version of their M1A Supermatch rifle with a McMillan Stock and match grade barrel and dubbed it the "M-25 White Feather." The rifle had a likeness of Hathcock's signature and his "White Feather Logo" marked on the receiver.
Turner Saddlery similarly honored Hathcock by producing a line of leather rifle slings based on his design. The slings are embossed with Hathcock's signature.
On 9 March 2007, the rifle and pistol complex at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar was officially renamed the Carlos Hathcock Range Complex.
Books (Non-Fiction)
Hathcock was the subject of a number of books including:
Chandler, Roy F. (1997). White feather: Carlos Hathcock USMC scout sniper : an authorized biographical memoir (1997 ed.). Iron Brigade Armory Publishing. Total pages: 277
Henderson, Charles (2001). Marine Sniper: 93 Confirmed Kills (2001 ed.). Berkley Books. Total pages: 315
Henderson, Charles W. (2003). Silent Warrior (2003 ed.). Berkley Books. Total pages: 336
Sasser, Charles; Roberts, Craig (1990). One Shot, One Kill (1990 ed.). Pocket Books. Total pages: 288
Fictional Works
Hathcock's career as a sniper has been used as a basis for a variety of fictional snipers from the "shooting through the scope incident" to the number of kills he made. There is a reference to Hathcock in the television show NCIS during the episode "One Shot One Kill," when a small white feather is found at the crime scenes of a sniper's victims. Gibbs, a former Marine, credits Hathcock with "39 confirmed kills," apparently having transposed the digits of Hathcock's actual 93 confirmed kills.
The protagonist of Stephen Hunter's Bob Lee Swagger Series consisting of the novels Point of Impact, Black Light, Time to Hunt and I, Sniper is loosely based on Carlos Hathcock (Hathcock is alluded to in the book as "Gunny Sgt Carl Hitchcock".)
The 1993 movie Sniper, featuring actor Tom Berenger, is based on Hathcock's exploits in Vietnam.
In JAG, Season 1, Episode 16 ("High Ground"), Gunnery Sergeant Ray Crockett (portrayed by Stephen McHattie) is based on Hathcock. The Gunny is a sniper instructor at Quantico Virginia who believes that he is being "forced out of the service" short of his retirement. He makes the statement that he "wrote most of the book" on sniper operations. The character, Rabb, refers to an incident where the Gunny pins down an NVA unit by killing their officer with the first shot. Lastly, Gunny Crockett is a winner of The Wimbledon Cup.
In the fourth episode of the first season of the CBS show Criminal Minds: Suspect Behavior, the criminal being chased by the Behavioral Analysis Unit's red cell team is a long-distance sniper killer, (played by Noel Fisher). Fisher sends Mick Rawson (played by Matt Ryan) of the BAU team a package containing a pager which he uses to notify Rawson of his next kills; he signs the package "Carlos Hathcock," which Rawson explains by sharing the tale of Hathcock's 93 kills and an incident during the Vietnam War in which he was put up against the best sniper of the NVA known only as 'Cobra'. (thus mimicking the incident since Rawson is also a skilled sniper shooter).
Civilian Life
Hathcock once said that he survived in his work because of an ability to "get in the bubble," to put himself into a state of "utter, complete, absolute concentration," first with his equipment, then his environment, in which every breeze and every leaf meant something, and finally on his quarry. After the war, a friend showed Hathcock a passage written by Ernest Hemingway: "Certainly there is no hunting like the hunting of man, and those who have hunted armed men long enough and like it, never really care for anything else thereafter." He copied Hemingway's words on a piece of paper. "He got that right," Hathcock said. "It was the hunt, not the killing." Hathcock said in a book written about his career as a sniper: "I like shooting, and I love hunting. But I never did enjoy killing anybody. It's my job. If I don't get those bastards, then they're gonna kill a lot of these kids dressed up like Marines. That's the way I look at it."
Hathcock's son, Carlos Hathcock III, would later enlist in the Marine Corps; he retired from the Marine Corps as a Gunnery Sergeant after following in his father's footsteps as a shooter, and became a member of the Board of Governors of the Marine Corps Distinguished Shooters Association.
Personal
Hathcock married Jo Winstead on 20 November 1962. Jo gave birth to a son, whom they named Carlos Norman Hathcock III.
Death and Burial
Gunnery Sergeant Carlos Norman Hathcock II died on 23 February 1999, in Virginia Beach, VA, after a long struggle with multiple sclerosis. He is buried at Woodlawn Memorial Gardens in Norfolk, VA."
he basic background information for this video's story is the sniper battle between the legendary American sniper Carlos Hathcock (AKA "White Feather") and the infamous NVA (North Vietnamese Army) sniper called "Cobra". White Feather and his spotter, John Burke, trail the deadly sniper through the jungle near the military base of Hill 55 in Da Nang, Vietnam, and they eventually manage to defeat the lone sniper by shooting through the scope of the NVA sniper.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S-prw33dyt0
FYI COL Mikel J. Burroughs LTC Stephen C. LTC Ivan Raiklin, Esq. Capt Seid Waddell Capt Tom Brown CW5 (Join to see) SGM David W. Carr LOM, DMSM MP SGT MSG Andrew White SFC William Farrell SSgt Robert Marx SSgt (Join to see) TSgt Joe C. SGT John " Mac " McConnell SP5 Mark Kuzinski SPC (Join to see) SrA Christopher Wright Cpl Joshua Caldwell SFC Joe S. Davis Jr., MSM, DSL
(4)
(0)
LTC Stephen F.
short bio on legendary Marine Corps sniper Carlos Hathcock
Short bio on legendary Marine Corps sniper Carlos Hathcock
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NmlXlddi06k
FYI LTC Bill Koski CW5 (Join to see) MSG Brad Sand SGM Steve Wettstein SSG James J. Palmer IV aka "JP4" SP5 Mark Kuzinski SrA Christopher Wright PO1 William "Chip" Nagel PO1 John Miller SP5 Robert Ruck SPC (Join to see) PO3 Steven Sherrill SN Greg Wright Maj Marty Hogan SCPO Morris Ramsey TSgt Joe C. Cpl Joshua Caldwell SGT Michael Thorin SP5 Dave (Shotgun) Shockley
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NmlXlddi06k
FYI LTC Bill Koski CW5 (Join to see) MSG Brad Sand SGM Steve Wettstein SSG James J. Palmer IV aka "JP4" SP5 Mark Kuzinski SrA Christopher Wright PO1 William "Chip" Nagel PO1 John Miller SP5 Robert Ruck SPC (Join to see) PO3 Steven Sherrill SN Greg Wright Maj Marty Hogan SCPO Morris Ramsey TSgt Joe C. Cpl Joshua Caldwell SGT Michael Thorin SP5 Dave (Shotgun) Shockley
(2)
(0)
I've heard about that method before, but I never knew Carlos coined it (of course maybe he didn't, but still). It'd be nice if we could zero our rifles like that for annual qualification.
(4)
(0)
Read This Next



 Rifle Shooting
Rifle Shooting Rifles
Rifles Sniper
Sniper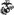 Marines
Marines





